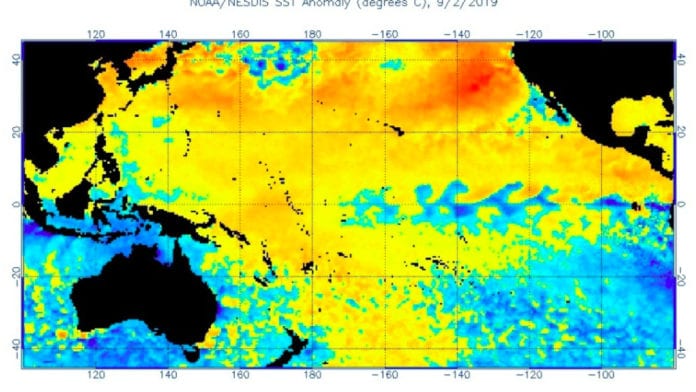
The ‘Blob’ refers to a stretch of ocean water in the pacific that is much hotter than the expected temperature of ocean water in the area. This anomaly was discovered in 2013, and ever since then, researchers have been trying to understand what caused this phenomenon. The blob itself is extremely dangerous to animal life as thousands of seabirds have washed up dead on shores as a direct consequence. The warmth of the water has driven away the salmon, krill, and other aquatic animals, which served as food to some of the predators of the ocean. Now starving baby sea lions have become the norm.
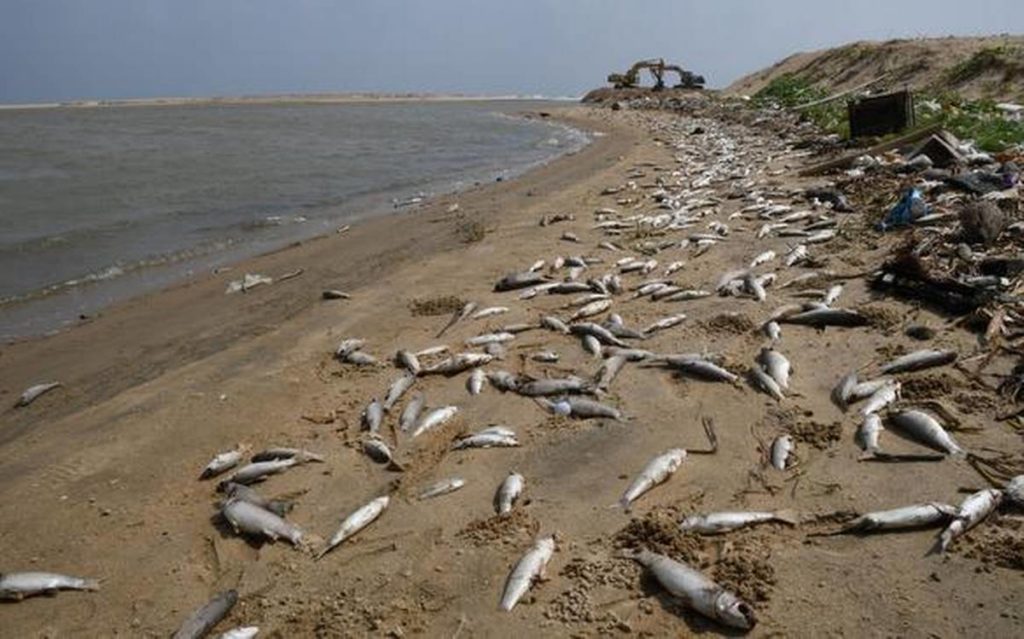

The effects of this phenomenon are not limited to animal life. The heat has helped the growth of toxic algae that are adversely affecting the different aquatic ecosystems of the ocean. The different ecosystems that coexist in the area are also responsible for keeping a lot of economic activity intact. One example of this is the dwindling number of crab fisheries. The sheer scale of devastation caused by this anomaly is damning as reportedly 100 Million Pacific cod are thought to have perished as a direct consequence of this blob.
The peak temperature of the blob reaches up to 4 degrees Celsius above the normal water temperature of the ocean. This particular phenomenon persisted until 2015. However, that is not the end of the story. Multiple such blobs are thought to have popped up around the world and have disturbed the marine ecosystem severely. Many conservation projects around the world have suffered setbacks due to this particular phenomenon. What is even worse is that new scientific evidence suggests that this is a direct consequence of the human impact on our planet’s climate. These occurrences are the direct result of the pollutants that we have set free.
The researchers have modeled these climate phenomena and tried to figure out how we are responsible for their occurrences. What the researchers found was that if there was no human-induced climate change, these blobs would only occur once in hundreds or thousands of years. The present observations indicate that these phenomena are not only rising in intensity but frequency as well, which could very spell disaster for a lot of aquatic animals out there. If we reach 3 degrees Celsius increase in average global temperature, the occurrence of these could become an annual event.
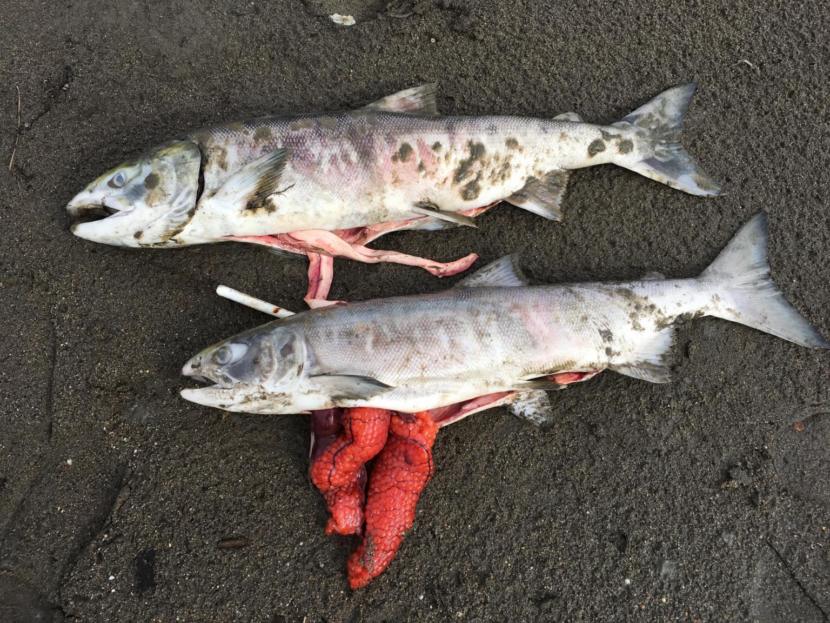

The massive loss of biodiversity and the shift in eating patterns of large amounts of the fauna worldwide will wreak havoc for the different ecosystems around the world. If things continue like this, the oceans will be a very different place than what they were in the past.
Further Reading: